The Universe By Numbers
Exponential or Scientific Notation:
It is easier to write very large numbers such as 100,000,000 as 108 (“1” followed by 8 “0”s).
Similarly very small numbers are written using negative exponents, e.g. 0.0000001 is 10-7 (the “1” is seven places to the right of the decimal point).
Bear in mind though that 109 is ten times the size of 108, and 1018 is ten billion times larger.
|
Some of the numbers, both small and large, that are bandied around in modern physics are very difficult to grasp. Below is a table listing - from the infinitesimally small to the incomprehensibly large - some of the numbers which are relevant to the subject matter.
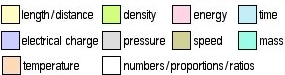
Obviously, the units used affects these numbers (e.g. meters, kilometers, miles, light years, etc), but I have tried to use consistent metric units throughout: meters for distance, seconds for time, meters/second for speed, degrees Kelvin for temperature, kilograms for mass, kilograms/meter3 for density, Joules for energy, Coulombs for electrical charge, kilopascals for pressure.
The different types of measurements are also color-coded for convenience:
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00054
|
5.4 × 10-44
|
Planck Time (in seconds), the shortest meaningful interval of time, and the earliest time the known universe can be measured from.
|
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001616
|
1.616 × 10-35
|
Planck Length (in meters), the size of a hypothetical string. Lengths smaller than this are considered not make any physical sense in our current understanding of physics.
|
0.000000000000000000000000000000911
|
9.11 × 10-31
|
Approximate mass (in kilograms) of a stationary electron.
|
0.000000000000000000000000001
|
1 × 10-27
|
Approximate density (in kg/meter3) of the universe as a whole.
|
0.000000000000000000000000001673
|
1.673 × 10-27
|
Approximate mass (in kilograms) of a proton.
|
0.000000000000000000000000001675
|
1.675 × 10-27
|
Approximate mass (in kilograms) of a neutron.
|
0.000000000000000000000000005
|
5 × 10-27
|
Estimated critical density (in kg/meter3) of the universe, to allow a steady state between expansion and contraction (about 5 × 10-30 g/cm3).
|
0.00000000000000000000002
|
2 × 10-23
|
Effective radius (in meters) of a neutrino particle.
|
0.0000000000000000001602
|
1.602 × 10-19
|
Elementary charge (in Coulombs), i.e. the negative charge of a single electron, or the positive charge of a single proton.
|
0.00000000000000000052
|
5.2 × 10-19
|
Approximate energy (in Joules) of photons in visible light.
|
0.000000000000000001
|
1 × 10-18
|
Upper limit (in meters) on the size of the quark particles that make up protons and neutrons.
|
0.000000000000000001
|
1 × 10-18
|
Smallest object observable and measurable by current science.
|
0.00000000000000001
|
1 × 10-17
|
Approximate density (in kg/meter3) of the best vacuum achievable in a laboratory.
|
0.000000000000002818
|
2.818 × 10-15
|
Effective radius (in meters) of an electron according to classical theory.
|
0.00000000000001
|
1 × 10-14
|
Range (in meters) of the weak nuclear force within the nucleus.
|
0.00000000000008187
|
8.187 × 10-14
|
Rest mass-energy (in Joules) of an electron.
|
0.000000000001
|
1 × 10-12
|
Approximate mass (in kilograms) of the average human cell.
|
0.000000000005
|
5 × 10-12
|
Longest wavelength (in meters) of gamma rays.
|
0.000000000025
|
2.5 × 10-11
|
Radius (in meters) of a hydrogen atom.
|
0.0000000005972
|
5.972 × 10-10
|
Rest mass-energy (in Joules) of an alpha particle.
|
0.0000004
|
4 × 10-7
|
Approximate wavelength (in meters) of violet light, the shortest in the visible spectrum.
|
0.0000007
|
7 × 10-7
|
Approximate wavelength (in meters) of red light, the long in the visible spectrum.
|
0.007297
|
7.297 × 10-3
|
The fine-structure constant, α, measuring the electromagnetic interaction between elementary particles.
|
0.74
|
7.4 × 10-1
|
Proportion of all matter in the universe composed of hydrogen.
|
0
|
0 × 100
|
Temperature (in ° Kelvin) of absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature (equivalent to -273.15° Celsius).
|
1.48
|
1.48 × 100
|
Density (in kg/meter3) of Earth’s atmosphere at sea level.
|
2.725
|
2.725 × 100
|
Temperature (in ° Kelvin) of cosmic microwave background radiation.
|
3.14
|
3.14 × 100
|
Pi, the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter (more accurately 3.14159265358979323846...)
|
9.8
|
9.8 × 100
|
Strength of the gravitational field (in meters/second/second) at the Earth's surface.
|
92
|
9.2 × 101
|
Number of naturally occurring elements.
|
100
|
1 × 102
|
Wavelength (in meters) of the lowest shortwave radio frequency.
|
101
|
1.01 × 102
|
Standard atmospheric pressure (in kilopascals) for Earth at sea level.
|
331
|
3.31 × 102
|
Speed (in meters/second) of sound in air at sea level and 0°C.
|
464
|
4.64 × 102
|
Speed (in meters/second) of the Earth's rotation at the equator.
|
1,000
|
1 × 103
|
Density (in kg/meter3) of liquid water at 4°C.
|
1,366
|
1.366 × 103
|
Total solar radiation (in Joules) received from the Sun by one square meter of the Earth's surface per second.
|
5,780
|
5.78 × 103
|
Temperature (in ° Kelvin) of the surface of the Sun.
|
29,800
|
2.98 × 104
|
Speed (in meters/second) of the Earth in orbit around the Sun.
|
145,000
|
1.45 × 105
|
Ratio of the size of an atom of hydrogen to its nucleus (the ration of other more complex atoms is less).
|
150,000
|
1.5 × 105
|
Density (in kg/meter3) of the core of the Sun.
|
200,000
|
2 × 105
|
Speed (in meters/second) of the Solar System in orbit around the Milky Way galaxy.
|
552,000
|
5.52 × 105
|
Speed of the Milky Way galaxy, relative to the cosmic microwave background radiation.
|
3,474,000
|
3.474 × 106
|
Diameter (in meters) of the Moon.
|
12,756,000
|
1.2756 × 107
|
Equatorial diameter (in meters) of the Earth.
|
15,600,000
|
1.56 × 107
|
Temperature (in ° Kelvin) at the core of the Sun.
|
299,792,458
|
2.998 × 108
|
Speed (in meters/second) of light (or any electromagnetic radiation) in a vacuum.
|
384,000,000
|
3.84 × 108
|
Orbital distance (in meters) of the Moon from the Earth.
|
1,000,000,000
|
1 × 109
|
Approximate density (in kg/meter3) of white dwarf, or dead, stars.
|
1,390,000,000
|
1.39 × 109
|
Diameter (in meters) of the Sun (1.39 million kilometers).
|
10,000,000,000
|
1 × 1010
|
Temperature (in ° Kelvin) in a supernova explosion.
|
80,000,000,000
|
8 × 1010
|
Rough estimate of the number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy (estimates vary up to 4 × 1011).
|
150,000,000,000
|
1.5 × 1011
|
Mean distance (in meters) between the Earth and the Sun (150 million kilometers, or 1 Astronomical Unit).
|
380,000,000,000
|
3.8 × 1011
|
Pressure (in kilopascals) inside the core of the Earth.
|
900,000,000,000
|
9 × 1011
|
Estimated optical diameter (in meters) of Betelgeuse, a red supergiant star.
|
3,000,000,000,000
|
3 × 1012
|
Estimated optical diameter (in meters) of VY Canis Majoris, a red hypergiant and the largest known star (about 2,000 times the size of our Sun).
|
10,000,000,000,000
|
1 × 1013
|
Approximate diameter (in meters) of the Solar System (10 billion kilometers).
|
20,000,000,000,000
|
2 × 1013
|
Approximate density (in kg/meter3) of the universe at the electroweak epoch, about 10–12 seconds after the Big Bang.
|
90,000,000,000,000
|
9 × 1013
|
Theoretical total mass-energy (in Joules) of one gram of matter.
|
100,000,000,000,000
|
1 × 1014
|
Estimated number of cells in the human body (9 out of every 10 being bacteria cells).
|
9,460,000,000,000,000
|
9.46 × 1015
|
Distance (in meters) traveled by light in one year (1 light year or 9.46 trillion kilometers).
|
25,000,000,000,000,000
|
2.5 × 1016
|
Pressure (in kilopascals) inside the core of the Sun.
|
40,000,000,000,000,000
|
4 × 1016
|
Distance (in meters) to Proxima Centauri, the nearest star after the Sun (about 4.23 light years).
|
141,000,000,000,000,000
|
1.41 × 1017
|
Half-life (in seconds) of uranium (4.468 billion years).
|
200,000,000,000,000,000
|
2 × 1017
|
Density (in kg/meter3) of atomic nuclei and neutron stars.
|
432,000,000,000,000,000
|
4.32 × 1017
|
Estimated age (in seconds) of the universe, assuming 13.7 billion years since the Big Bang.
|
1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
1 × 1021
|
Approximate diameter (in meters) of galactic disk of Milky Way galaxy (100,000 light years).
|
70,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
7 × 1022
|
Rough estimate of the number of stars in the observable universe (estimates vary from 1022 to 1024).
|
22,300,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
2.23 × 1022
|
Distance (in meters) to the Andromeda Galaxy, the nearest galaxy to our own (2.36 million light years).
|
2,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
2 × 1024
|
Diameter (in meters) of the Virgo Supercluster, the cluster of galaxies which includes our own Local Group of galaxies (about 200 million light years).
|
6,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
6 × 1024
|
Mass (in kilograms) of the Earth.
|
386,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
3.86 × 1026
|
Total energy output (in Joules) of the Sun each second.
|
880,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
8.8 × 1026
|
Approximate diameter (in meters) of the visible universe (93 billion light years).
|
1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
1 × 1027
|
Temperature (in ° Kelvin) of the universe 10-35 seconds after the Big Bang, at the start of the inflationary epoch.
|
2,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
2 × 1030
|
Mass (in kilograms) of the Sun (1 solar mass).
|
40,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
4 × 1031
|
Mass (in kilograms) of Betelgeuse, a red supergiant star (about 20 solar masses).
|
141,700,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
1.417 × 1032
|
Planck Temperature, the temperature (in ° Kelvin) of the universe at 1 Planck Time after the Big Bang.
|
10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000
|
1 × 1040
|
Approximate ratio of the strength of the electromagnetic to the gravitational force between sub-atomic particles.
|
36,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000
|
3.6 × 1040
|
Mass (in kilograms) of OJ287, the largest measured supermassive black hole.
|
687,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000
|
6.87 × 1041
|
Gravitational binding energy (in Joules) of the Sun.
|
120,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000
|
1.2 × 1044
|
Estimated energy (in Joules) released in a supernova explosion.
|
30,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000,000,000,000
|
3 × 1052
|
Estimated mass (in kilograms) of the observable universe.
|
4,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000
|
4 × 1069
|
Estimated total mass-energy (in Joules) of the observable universe.
|
100,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000
|
1 × 1080
|
Estimate the total number of fundamental particles in the observable universe (other estimates go up to 1085).
|
5,100,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
|
5.1 × 1096
|
Planck density, the density (in kg/meter3) of the universe at one unit of Planck time after the Big Bang.
|
|